This blog is for beginner who doesn’t have any idea how software works. If you are starting your computer journey this might be helpful.
What’s the first thing we do if you want to run the Firefox and it’s not in your machine/computer/OS?
Ans: You just search Firefox and download the executable file and install it and run it.
Have you ever wonder what happen when you install the executable???
Installation
- When we install software on our operating system, we are essentially setting up the necessary files, libraries, and configurations required for the software to run properly.
- The installation process typically involves copying the software’s files to specific locations on the disk, configuring the operating system to recognize and interact with the software, and sometimes installing additional dependencies that the software relies on.
- Lets take an example of Firefox:
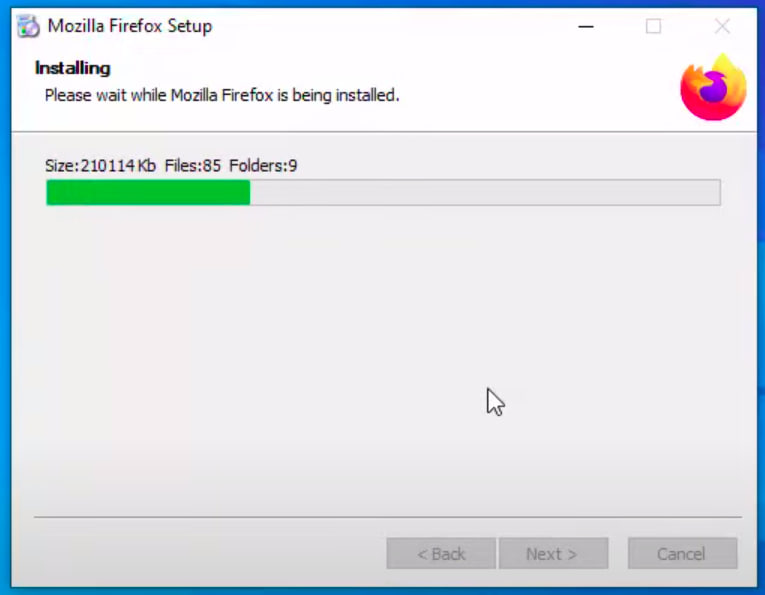
- If you are installing Firefox on windows OS: - You download a Firefox installer executable - You execute Firefox installer - If you have noticed you might see files are being copied to C:/Program File/firefox/… - On copying files to C:/Program File/firefox your windows OS will know how a Firefox can execute
- If you are installing Firefox in *nix OS: - You download a Firefox installer executable - You execute Firefox installer - If you have noticed you might see that your Firefox binary is at
/bin/firefox(output of$ which firefox) - As you might have guessed already, yep OS know the path/bin/so you can run the program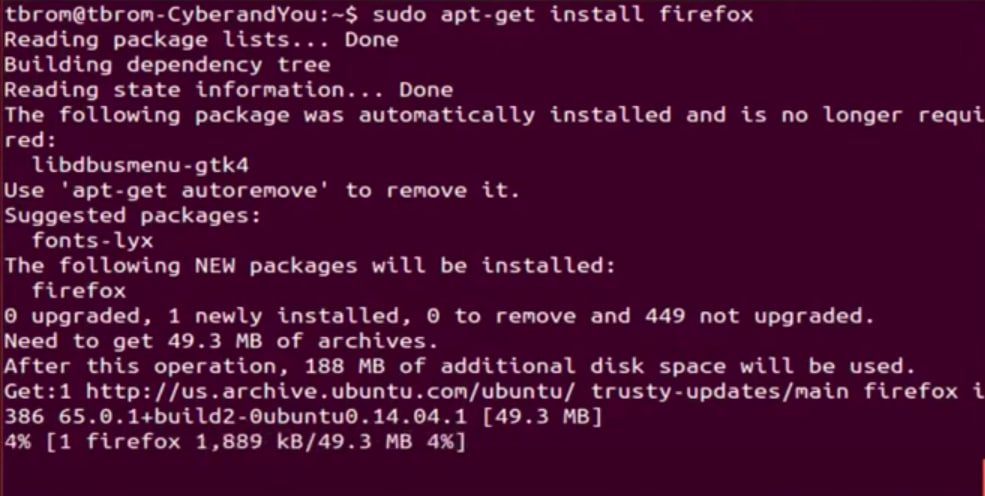
- If you are installing Firefox on windows OS: - You download a Firefox installer executable - You execute Firefox installer - If you have noticed you might see files are being copied to C:/Program File/firefox/… - On copying files to C:/Program File/firefox your windows OS will know how a Firefox can execute
- In sort; in installation phase OS just copy the necessary files which are required to run the program to a specific location or folder so that now you can run the program
Execution
- After the software is installed, it can be executed by the operating system or launched through a user interface [it can be GUI or CLI]
- When we run the software,
- the operating system analyzes the constrains to run the program (i.e. necessary memory, CPU, GPU, dependencies) then
- loads the necessary files into memory and starts executing the instructions provided by the software
- If the constrains didn’t satisfy it will either throw the error specifying exact error or throw warning but work
- The software utilizes the system’s resources, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network, to perform its intended tasks
Note:
- When your software, application, or package is located in a place where your OS can execute it, it is called a program
- When you run the
Programthe necessary files are loaded into memory [Primary Memory: RAM] it will become Process - “Program” in execution is referred to “Process”
Dependency
TLDR; dependencies play a crucial role in software development and deployment by providing the required functionality, compatibility, and efficiency needed for the software to run successfully on the operating system.
- Dependencies are external software components or libraries that the software relies on to function correctly
- These dependencies provide additional functionality or services that the software needs to operate
- For example, a software application might depend on a specific version of a database engine, a programming language runtime, or a set of libraries for graphical user interface (GUI) functionality
- When a software application has dependencies, it means that it requires the presence of specific software components or libraries to be installed on the operating system in order to run successfully
- Without these dependencies, the software may encounter errors or fail to function properly
- Dependencies are needed for several reasons:
- Functionality:
- provide additional features or services that the software requires to perform its intended tasks
- or example, a web application might depend on a web server software or a database engine to handle HTTP requests or store data
- in case if you have done C you can think like this: to run the printf() you need to include stdio.h.
- Code Reusability:
- allow software developers to leverage existing libraries or frameworks to avoid reinventing the wheel
- by relying on well-established dependencies, developers can focus on the unique aspects of their software without having to implement every feature from scratch
- in case if you have done C you can think like this: to run the printf() after including stdio.h you don’t need to implement the printf() logic
- Compatibility and Stability:
- ensure that the software is compatible with specific versions of other software components
- provide a consistent and tested environment for the software to run, reducing the chances of conflicts or compatibility issues
- in case if you have done C you can think like this: you can run printf() after including stdio.h you don’t need to worry about version of C language
- Efficiency:
- allow software developers to use optimized and specialized libraries for specific tasks, improving the performance and efficiency of the software
- for example, a graphics-intensive application might rely on a graphics processing library to accelerate rendering
- Functionality:
Since OS, is also a software or application which manages other application it also have lots of dependencies.
As you might have already guess, managing dependencies is essential to ensure that the software runs correctly. In traditional software installations, dependencies are often installed manually or bundled with the software package(software installer).
However, with containerization technologies like Docker, dependencies can be included in the container image, providing a self-contained and reproducible environment for running software without worrying about conflicting dependencies or system-specific configurations.
Next time you install the software/application/package do notice what are being copied and check the RAM usage after executing the application after installation.
Thank you for reading!!!